Dans ce didacticiel, vous apprendrez ce qu'est un arbre avl. Vous trouverez également des exemples de travail de diverses opérations effectuées sur une arborescence avl en C, C ++, Java et Python.
L'arbre AVL est un arbre de recherche binaire auto-équilibré dans lequel chaque nœud conserve des informations supplémentaires appelées un facteur d'équilibre dont la valeur est -1, 0 ou +1.
L'arbre AVL tire son nom de son inventeur Georgy Adelson-Velsky et Landis.
Facteur d'équilibre
Le facteur d'équilibre d'un nœud dans un arbre AVL est la différence entre la hauteur du sous-arbre gauche et celle du sous-arbre droit de ce nœud.
Facteur d'équilibre = (Hauteur du sous-arbre gauche - Hauteur du sous-arbre droit) ou (Hauteur du sous-arbre droit - Hauteur du sous-arbre gauche)
La propriété d'auto-équilibrage d'un arbre avl est maintenue par le facteur d'équilibre. La valeur du facteur d'équilibre doit toujours être -1, 0 ou +1.
Un exemple d'arborescence avl équilibrée est:
 Arbre Avl
Arbre Avl
Opérations sur une arborescence AVL
Les différentes opérations qui peuvent être effectuées sur une arborescence AVL sont:
Rotation des sous-arbres dans une arborescence AVL
En rotation, les positions des nœuds d'un sous-arbre sont interchangées.
Il existe deux types de rotations:
Rotation à gauche
En rotation à gauche, la disposition des nœuds à droite est transformée en dispositions sur le nœud de gauche.
Algorithme
- Soit l'arbre initial:
 Rotation à gauche
Rotation à gauche - Si y a un sous-arbre gauche, assignez x comme parent du sous-arbre gauche de y.
 Assignez x comme parent du sous-arbre gauche de y
Assignez x comme parent du sous-arbre gauche de y - Si le parent de x est
NULL, faites de y la racine de l'arbre. - Sinon, si x est l'enfant gauche de p, faites y comme enfant gauche de p.
- Sinon, attribuez y comme le bon enfant de p.
 Changer le parent de x en celui de y
Changer le parent de x en celui de y - Faites de y le parent de x.
 Affectez y comme parent de x.
Affectez y comme parent de x.
Rotation à droite
En rotation gauche, la disposition des nœuds à gauche est transformée en dispositions sur le nœud droit.
- Soit l'arbre initial:
 Arbre initial
Arbre initial - Si x a un sous-arbre droit, affectez y comme parent du sous-arbre droit de x.
 Assignez y comme parent du sous-arbre droit de x
Assignez y comme parent du sous-arbre droit de x - Si le parent de y est
NULL, faites x comme racine de l'arbre. - Sinon, si y est le bon enfant de son parent p, faites de x le bon enfant de p.
- Sinon, attribuez x comme enfant gauche de p.
 Assignez le parent de y comme parent de x.
Assignez le parent de y comme parent de x. - Faites de x le parent de y.
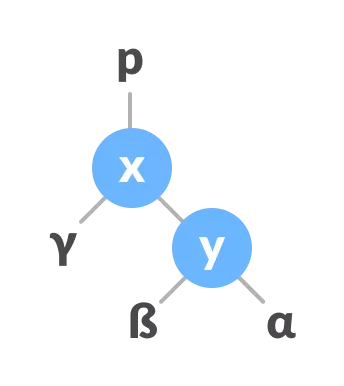 Attribuer x comme parent de y
Attribuer x comme parent de y
Rotation gauche-droite et droite-gauche
Dans la rotation gauche-droite, les dispositions sont d'abord décalées vers la gauche, puis vers la droite.
- Faites une rotation à gauche sur xy.
 Rotation gauche xy
Rotation gauche xy - Faites une rotation à droite sur yz.
 Rotation à droite zy
Rotation à droite zy
En rotation droite-gauche, les dispositions sont d'abord décalées vers la droite, puis vers la gauche.
- Faites une rotation à droite sur xy.
 Rotation à droite xy
Rotation à droite xy - Faites une rotation à gauche sur zy.
 Rotation gauche zy
Rotation gauche zy
Algorithme pour insérer un nouveau nœud
Un newNode est toujours inséré en tant que nœud feuille avec un facteur d'équilibre égal à 0.
- Soit l'arbre initial:
 Arbre initial à insérer
Arbre initial à insérer
Soit le nœud à insérer: Nouveau nœud
Nouveau nœud - Accédez au nœud feuille approprié pour insérer un nouveau nœud en utilisant les étapes récursives suivantes. Comparez newKey avec rootKey de l'arborescence actuelle.
- Si newKey <rootKey, appelez l'algorithme d'insertion sur le sous-arbre gauche du nœud actuel jusqu'à ce que le nœud feuille soit atteint.
- Sinon, si newKey> rootKey, appelez l'algorithme d'insertion sur le sous-arbre droit du nœud actuel jusqu'à ce que le nœud feuille soit atteint.
- Sinon, retournez leafNode.
 Recherche de l'emplacement pour insérer un nouveau nœud
Recherche de l'emplacement pour insérer un nouveau nœud
- Comparez leafKey obtenu à partir des étapes ci-dessus avec newKey:
- Si newKey <leafKey, définissez newNode comme leftChild de leafNode.
- Sinon, définissez newNode comme rightChild de leafNode.
 Insertion du nouveau nœud
Insertion du nouveau nœud
- Mettre à jour balanceFactor des nœuds.
 Mise à jour du facteur d'équilibre après l'insertion
Mise à jour du facteur d'équilibre après l'insertion - Si les nœuds sont déséquilibrés, rééquilibrez le nœud.
- Si balanceFactor> 1, cela signifie que la hauteur du sous-arbre gauche est supérieure à celle du sous-arbre droit. Alors, faites une rotation droite ou gauche-droite
- Si newNodeKey <leftChildKey effectue une rotation à droite.
- Sinon, effectuez une rotation gauche-droite.
 Équilibrer l'arbre avec rotation
Équilibrer l'arbre avec rotation 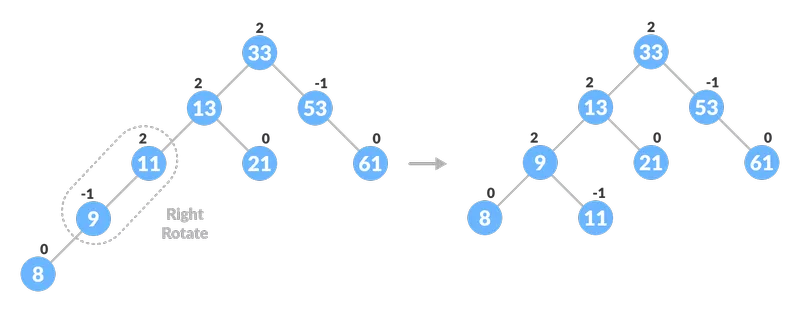 Équilibrer l'arbre avec rotation
Équilibrer l'arbre avec rotation
- Si balanceFactor <-1, cela signifie que la hauteur du sous-arbre droit est supérieure à celle du sous-arbre gauche. Alors, faites une rotation droite ou une rotation droite-gauche
- Si newNodeKey> rightChildKey, effectuez une rotation à gauche.
- Sinon, faites une rotation droite-gauche
- Si balanceFactor> 1, cela signifie que la hauteur du sous-arbre gauche est supérieure à celle du sous-arbre droit. Alors, faites une rotation droite ou gauche-droite
- L'arbre final est:
 Arbre final équilibré
Arbre final équilibré
Algorithme pour supprimer un nœud
Un nœud est toujours supprimé en tant que nœud feuille. Après la suppression d'un nœud, les facteurs d'équilibre des nœuds sont modifiés. Afin de rééquilibrer le facteur d'équilibre, des rotations appropriées sont effectuées.
- Localisez nodeToBeDeleted (la récursivité est utilisée pour trouver nodeToBeDeleted dans le code utilisé ci-dessous).
 Localisation du nœud à supprimer
Localisation du nœud à supprimer - Il existe trois cas de suppression d'un nœud:
- Si nodeToBeDeleted est le nœud feuille (c'est-à-dire qu'il n'a pas d'enfant), alors supprimez nodeToBeDeleted.
- Si nodeToBeDeleted a un enfant, remplacez le contenu de nodeToBeDeleted par celui de l'enfant. Retirez l'enfant.
- Si nodeToBeDeleted a deux enfants, recherchez le successeur inorder w de nodeToBeDeleted (ie. Node avec une valeur minimale de clé dans le sous-arbre de droite).
 Trouver le successeur
Trouver le successeur
- Remplacez le contenu de nodeToBeDeleted par celui de w.
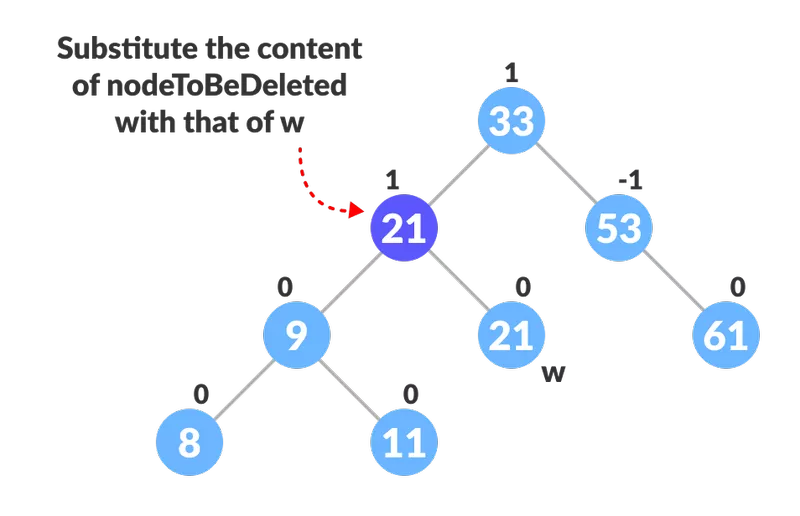 Remplacez le nœud à supprimer
Remplacez le nœud à supprimer - Supprimez le nœud feuille w.
 Supprimer w
Supprimer w
- Remplacez le contenu de nodeToBeDeleted par celui de w.
- Mettre à jour balanceFactor des nœuds.
 Mettre à jour bf
Mettre à jour bf - Rééquilibrez l'arbre si le facteur d'équilibre de l'un des nœuds n'est pas égal à -1, 0 ou 1.
- Si balanceFactor of currentNode> 1,
- Si balanceFactor of leftChild> = 0, effectuez une rotation à droite.
 Rotation à droite pour équilibrer l'arbre
Rotation à droite pour équilibrer l'arbre - Sinon, faites une rotation gauche-droite.
- Si balanceFactor of leftChild> = 0, effectuez une rotation à droite.
- Si balanceFactor of currentNode <-1,
- Si balanceFactor of rightChild <= 0, effectuez une rotation à gauche.
- Sinon, faites une rotation droite-gauche.
- Si balanceFactor of currentNode> 1,
- L'arbre final est:
 Avl tree final
Avl tree final
Exemples Python, Java et C / C ++
Python Java C C ++ # AVL tree implementation in Python import sys # Create a tree node class TreeNode(object): def __init__(self, key): self.key = key self.left = None self.right = None self.height = 1 class AVLTree(object): # Function to insert a node def insert_node(self, root, key): # Find the correct location and insert the node if not root: return TreeNode(key) elif key 1: if key < root.left.key: return self.rightRotate(root) else: root.left = self.leftRotate(root.left) return self.rightRotate(root) if balanceFactor root.right.key: return self.leftRotate(root) else: root.right = self.rightRotate(root.right) return self.leftRotate(root) return root # Function to delete a node def delete_node(self, root, key): # Find the node to be deleted and remove it if not root: return root elif key root.key: root.right = self.delete_node(root.right, key) else: if root.left is None: temp = root.right root = None return temp elif root.right is None: temp = root.left root = None return temp temp = self.getMinValueNode(root.right) root.key = temp.key root.right = self.delete_node(root.right, temp.key) if root is None: return root # Update the balance factor of nodes root.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(root.left), self.getHeight(root.right)) balanceFactor = self.getBalance(root) # Balance the tree if balanceFactor> 1: if self.getBalance(root.left)>= 0: return self.rightRotate(root) else: root.left = self.leftRotate(root.left) return self.rightRotate(root) if balanceFactor < -1: if self.getBalance(root.right) <= 0: return self.leftRotate(root) else: root.right = self.rightRotate(root.right) return self.leftRotate(root) return root # Function to perform left rotation def leftRotate(self, z): y = z.right T2 = y.left y.left = z z.right = T2 z.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(z.left), self.getHeight(z.right)) y.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(y.left), self.getHeight(y.right)) return y # Function to perform right rotation def rightRotate(self, z): y = z.left T3 = y.right y.right = z z.left = T3 z.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(z.left), self.getHeight(z.right)) y.height = 1 + max(self.getHeight(y.left), self.getHeight(y.right)) return y # Get the height of the node def getHeight(self, root): if not root: return 0 return root.height # Get balance factore of the node def getBalance(self, root): if not root: return 0 return self.getHeight(root.left) - self.getHeight(root.right) def getMinValueNode(self, root): if root is None or root.left is None: return root return self.getMinValueNode(root.left) def preOrder(self, root): if not root: return print("(0) ".format(root.key), end="") self.preOrder(root.left) self.preOrder(root.right) # Print the tree def printHelper(self, currPtr, indent, last): if currPtr != None: sys.stdout.write(indent) if last: sys.stdout.write("R----") indent += " " else: sys.stdout.write("L----") indent += "| " print(currPtr.key) self.printHelper(currPtr.left, indent, False) self.printHelper(currPtr.right, indent, True) myTree = AVLTree() root = None nums = (33, 13, 52, 9, 21, 61, 8, 11) for num in nums: root = myTree.insert_node(root, num) myTree.printHelper(root, "", True) key = 13 root = myTree.delete_node(root, key) print("After Deletion: ") myTree.printHelper(root, "", True)
// AVL tree implementation in Java // Create node class Node ( int item, height; Node left, right; Node(int d) ( item = d; height = 1; ) ) // Tree class class AVLTree ( Node root; int height(Node N) ( if (N == null) return 0; return N.height; ) int max(int a, int b) ( return (a> b) ? a : b; ) Node rightRotate(Node y) ( Node x = y.left; Node T2 = x.right; x.right = y; y.left = T2; y.height = max(height(y.left), height(y.right)) + 1; x.height = max(height(x.left), height(x.right)) + 1; return x; ) Node leftRotate(Node x) ( Node y = x.right; Node T2 = y.left; y.left = x; x.right = T2; x.height = max(height(x.left), height(x.right)) + 1; y.height = max(height(y.left), height(y.right)) + 1; return y; ) // Get balance factor of a node int getBalanceFactor(Node N) ( if (N == null) return 0; return height(N.left) - height(N.right); ) // Insert a node Node insertNode(Node node, int item) ( // Find the position and insert the node if (node == null) return (new Node(item)); if (item node.item) node.right = insertNode(node.right, item); else return node; // Update the balance factor of each node // And, balance the tree node.height = 1 + max(height(node.left), height(node.right)); int balanceFactor = getBalanceFactor(node); if (balanceFactor> 1) ( if (item node.left.item) ( node.left = leftRotate(node.left); return rightRotate(node); ) ) if (balanceFactor node.right.item) ( return leftRotate(node); ) else if (item < node.right.item) ( node.right = rightRotate(node.right); return leftRotate(node); ) ) return node; ) Node nodeWithMimumValue(Node node) ( Node current = node; while (current.left != null) current = current.left; return current; ) // Delete a node Node deleteNode(Node root, int item) ( // Find the node to be deleted and remove it if (root == null) return root; if (item root.item) root.right = deleteNode(root.right, item); else ( if ((root.left == null) || (root.right == null)) ( Node temp = null; if (temp == root.left) temp = root.right; else temp = root.left; if (temp == null) ( temp = root; root = null; ) else root = temp; ) else ( Node temp = nodeWithMimumValue(root.right); root.item = temp.item; root.right = deleteNode(root.right, temp.item); ) ) if (root == null) return root; // Update the balance factor of each node and balance the tree root.height = max(height(root.left), height(root.right)) + 1; int balanceFactor = getBalanceFactor(root); if (balanceFactor> 1) ( if (getBalanceFactor(root.left)>= 0) ( return rightRotate(root); ) else ( root.left = leftRotate(root.left); return rightRotate(root); ) ) if (balanceFactor < -1) ( if (getBalanceFactor(root.right) <= 0) ( return leftRotate(root); ) else ( root.right = rightRotate(root.right); return leftRotate(root); ) ) return root; ) void preOrder(Node node) ( if (node != null) ( System.out.print(node.item + " "); preOrder(node.left); preOrder(node.right); ) ) // Print the tree private void printTree(Node currPtr, String indent, boolean last) ( if (currPtr != null) ( System.out.print(indent); if (last) ( System.out.print("R----"); indent += " "; ) else ( System.out.print("L----"); indent += "| "; ) System.out.println(currPtr.item); printTree(currPtr.left, indent, false); printTree(currPtr.right, indent, true); ) ) // Driver code public static void main(String() args) ( AVLTree tree = new AVLTree(); tree.root = tree.insertNode(tree.root, 33); tree.root = tree.insertNode(tree.root, 13); tree.root = tree.insertNode(tree.root, 53); tree.root = tree.insertNode(tree.root, 9); tree.root = tree.insertNode(tree.root, 21); tree.root = tree.insertNode(tree.root, 61); tree.root = tree.insertNode(tree.root, 8); tree.root = tree.insertNode(tree.root, 11); tree.printTree(tree.root, "", true); tree.root = tree.deleteNode(tree.root, 13); System.out.println("After Deletion: "); tree.printTree(tree.root, "", true); ) )
// AVL tree implementation in C #include #include // Create Node struct Node ( int key; struct Node *left; struct Node *right; int height; ); int max(int a, int b); // Calculate height int height(struct Node *N) ( if (N == NULL) return 0; return N->height; ) int max(int a, int b) ( return (a> b) ? a : b; ) // Create a node struct Node *newNode(int key) ( struct Node *node = (struct Node *) malloc(sizeof(struct Node)); node->key = key; node->left = NULL; node->right = NULL; node->height = 1; return (node); ) // Right rotate struct Node *rightRotate(struct Node *y) ( struct Node *x = y->left; struct Node *T2 = x->right; x->right = y; y->left = T2; y->height = max(height(y->left), height(y->right)) + 1; x->height = max(height(x->left), height(x->right)) + 1; return x; ) // Left rotate struct Node *leftRotate(struct Node *x) ( struct Node *y = x->right; struct Node *T2 = y->left; y->left = x; x->right = T2; x->height = max(height(x->left), height(x->right)) + 1; y->height = max(height(y->left), height(y->right)) + 1; return y; ) // Get the balance factor int getBalance(struct Node *N) ( if (N == NULL) return 0; return height(N->left) - height(N->right); ) // Insert node struct Node *insertNode(struct Node *node, int key) ( // Find the correct position to insertNode the node and insertNode it if (node == NULL) return (newNode(key)); if (key key) node->left = insertNode(node->left, key); else if (key> node->key) node->right = insertNode(node->right, key); else return node; // Update the balance factor of each node and // Balance the tree node->height = 1 + max(height(node->left), height(node->right)); int balance = getBalance(node); if (balance> 1 && key left->key) return rightRotate(node); if (balance node->right->key) return leftRotate(node); if (balance> 1 && key> node->left->key) ( node->left = leftRotate(node->left); return rightRotate(node); ) if (balance < -1 && key right->key) ( node->right = rightRotate(node->right); return leftRotate(node); ) return node; ) struct Node *minValueNode(struct Node *node) ( struct Node *current = node; while (current->left != NULL) current = current->left; return current; ) // Delete a nodes struct Node *deleteNode(struct Node *root, int key) ( // Find the node and delete it if (root == NULL) return root; if (key key) root->left = deleteNode(root->left, key); else if (key> root->key) root->right = deleteNode(root->right, key); else ( if ((root->left == NULL) || (root->right == NULL)) ( struct Node *temp = root->left ? root->left : root->right; if (temp == NULL) ( temp = root; root = NULL; ) else *root = *temp; free(temp); ) else ( struct Node *temp = minValueNode(root->right); root->key = temp->key; root->right = deleteNode(root->right, temp->key); ) ) if (root == NULL) return root; // Update the balance factor of each node and // balance the tree root->height = 1 + max(height(root->left), height(root->right)); int balance = getBalance(root); if (balance> 1 && getBalance(root->left)>= 0) return rightRotate(root); if (balance> 1 && getBalance(root->left) left = leftRotate(root->left); return rightRotate(root); ) if (balance right) <= 0) return leftRotate(root); if (balance right)> 0) ( root->right = rightRotate(root->right); return leftRotate(root); ) return root; ) // Print the tree void printPreOrder(struct Node *root) ( if (root != NULL) ( printf("%d ", root->key); printPreOrder(root->left); printPreOrder(root->right); ) ) int main() ( struct Node *root = NULL; root = insertNode(root, 2); root = insertNode(root, 1); root = insertNode(root, 7); root = insertNode(root, 4); root = insertNode(root, 5); root = insertNode(root, 3); root = insertNode(root, 8); printPreOrder(root); root = deleteNode(root, 3); printf("After deletion: "); printPreOrder(root); return 0; )
// AVL tree implementation in C++ #include using namespace std; class Node ( public: int key; Node *left; Node *right; int height; ); int max(int a, int b); // Calculate height int height(Node *N) ( if (N == NULL) return 0; return N->height; ) int max(int a, int b) ( return (a> b) ? a : b; ) // New node creation Node *newNode(int key) ( Node *node = new Node(); node->key = key; node->left = NULL; node->right = NULL; node->height = 1; return (node); ) // Rotate right Node *rightRotate(Node *y) ( Node *x = y->left; Node *T2 = x->right; x->right = y; y->left = T2; y->height = max(height(y->left), height(y->right)) + 1; x->height = max(height(x->left), height(x->right)) + 1; return x; ) // Rotate left Node *leftRotate(Node *x) ( Node *y = x->right; Node *T2 = y->left; y->left = x; x->right = T2; x->height = max(height(x->left), height(x->right)) + 1; y->height = max(height(y->left), height(y->right)) + 1; return y; ) // Get the balance factor of each node int getBalanceFactor(Node *N) ( if (N == NULL) return 0; return height(N->left) - height(N->right); ) // Insert a node Node *insertNode(Node *node, int key) ( // Find the correct postion and insert the node if (node == NULL) return (newNode(key)); if (key key) node->left = insertNode(node->left, key); else if (key> node->key) node->right = insertNode(node->right, key); else return node; // Update the balance factor of each node and // balance the tree node->height = 1 + max(height(node->left), height(node->right)); int balanceFactor = getBalanceFactor(node); if (balanceFactor> 1) ( if (key left->key) ( return rightRotate(node); ) else if (key> node->left->key) ( node->left = leftRotate(node->left); return rightRotate(node); ) ) if (balanceFactor node->right->key) ( return leftRotate(node); ) else if (key right->key) ( node->right = rightRotate(node->right); return leftRotate(node); ) ) return node; ) // Node with minimum value Node *nodeWithMimumValue(Node *node) ( Node *current = node; while (current->left != NULL) current = current->left; return current; ) // Delete a node Node *deleteNode(Node *root, int key) ( // Find the node and delete it if (root == NULL) return root; if (key key) root->left = deleteNode(root->left, key); else if (key> root->key) root->right = deleteNode(root->right, key); else ( if ((root->left == NULL) || (root->right == NULL)) ( Node *temp = root->left ? root->left : root->right; if (temp == NULL) ( temp = root; root = NULL; ) else *root = *temp; free(temp); ) else ( Node *temp = nodeWithMimumValue(root->right); root->key = temp->key; root->right = deleteNode(root->right, temp->key); ) ) if (root == NULL) return root; // Update the balance factor of each node and // balance the tree root->height = 1 + max(height(root->left), height(root->right)); int balanceFactor = getBalanceFactor(root); if (balanceFactor> 1) ( if (getBalanceFactor(root->left)>= 0) ( return rightRotate(root); ) else ( root->left = leftRotate(root->left); return rightRotate(root); ) ) if (balanceFactor right) right = rightRotate(root->right); return leftRotate(root); ) ) return root; ) // Print the tree void printTree(Node *root, string indent, bool last) ( if (root != nullptr) ( cout << indent; if (last) ( cout << "R----"; indent += " "; ) else ( cout << "L----"; indent += "| "; ) cout right, indent, true); ) ) int main() ( Node *root = NULL; root = insertNode(root, 33); root = insertNode(root, 13); root = insertNode(root, 53); root = insertNode(root, 9); root = insertNode(root, 21); root = insertNode(root, 61); root = insertNode(root, 8); root = insertNode(root, 11); printTree(root, "", true); root = deleteNode(root, 13); cout << "After deleting " << endl; printTree(root, "", true); )
Complexité des différentes opérations sur une arborescence AVL
| Insertion | Effacement | Chercher |
| O (log n) | O (log n) | O (log n) |
Applications de l'arborescence AVL
- Pour indexer des enregistrements volumineux dans des bases de données
- Pour rechercher dans de grandes bases de données








